How Deep Do Green Beans Roots Grow? Can They Grow in Shallow Soil?

Green beans are easy to grow and can be grown from seed or from transplants. Bush green beans should be spaced about four inches apart when planting, with rows being at least 18 inches apart.
Pole green beans require some kind of support, like a trellis or fence, because they can grow to heights of 6 feet! Runner beans need something even more sturdy, like a tepee-style structure, because they will reach 8 feet high if given the right conditions.
All types of green beans should be planted after all danger of frost has passed and the soil is warm enough for germination.
Despite the general familiarity with green beans, many people don’t know how deep green bean roots grow.
To gain a better understanding of this oft-underappreciated plant component, let’s take a closer look at the intricate root systems of green beans.
Introduction to Green Beans and Their Growth Habits
Green beans, also known as string beans or snap beans, are a type of legume that is often grown for their edible immature seeds and pods. These beans are usually picked and eaten while they are still young and tender, before the seeds inside have had a chance to fully mature.
Green beans are often grown in home gardens and are a popular ingredient in many dishes, from salads and stir-fries to soups and casseroles.
The plant that makes green beans is an annual plant, which means that it goes through its whole green beans life cycle in one growing season. It typically grows to be around two to three feet tall, and has narrow, elongated leaves that are a vibrant shade of green.
The plant produces small white or yellow flowers, which give way to the young green bean pods.
To grow green beans, it is best to plant the seeds in a location that receives plenty of sunlight and has well-draining soil. Green beans are not particularly picky when it comes to soil, but they do prefer a pH between 6.0 and 6.8.
It is also important to keep the plants watered, but not too much, as excess moisture can lead to the development of fungal diseases.
Once the plants are established, they will begin to produce their green bean pods. These pods will continue to grow and mature throughout the season, and can be harvested regularly for fresh eating. Green beans are a versatile and tasty addition to any garden, and with a little care and attention, they can provide a bountiful harvest.
The Role of Roots in Green Bean Plant Growth and Development
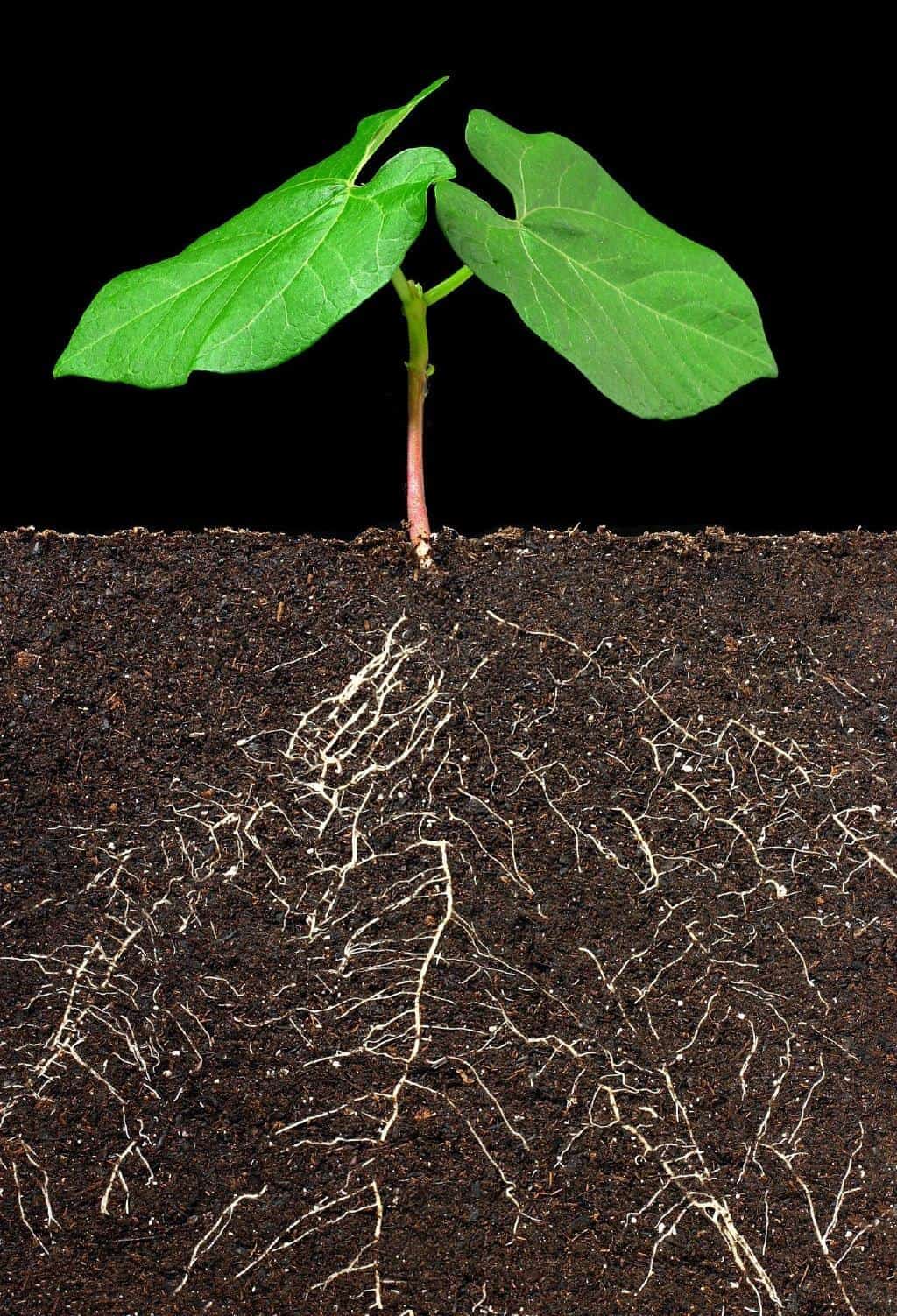
The roots of a green bean plant play a vital role in the overall growth and development of the plant. The roots’ main job is to hold the plant down in the ground and give it support.
As the plant gets taller, its root system spreads out to make sure it can get enough of these important nutrients. This is why it’s important to give your green beans plenty of space so that their root systems can spread out properly
The roots of a green bean plant do more than just hold the plant up. They also take in water and nutrients from the soil. These nutrients are then transported to the rest of the plant, where they are used to support growth and development. This process is known as nutrient uptake, and it is essential for the healthy growth of green beans.
Another important function of the roots of a green bean plant is to help the plant access water and moisture from the soil. Green beans need to be watered often to grow well, and the roots of the plant help make sure it gets enough water. This is especially important during dry spells, when the roots may need to reach deep into the soil to access moisture.
| In summary, the roots of a green bean plant play a crucial role in the growth and development of the plant. They give the plant support, help it take in nutrients, and help it get water, all of which are important for healthy growth and a good harvest. |
How Deep Do Green Bean Roots Typically Grow?
Green bean roots grow between 6 and 10 inches below the surface, which is not as deep as the roots of some other plants.
In fact, when cultivated in commercial fields or home gardens where green beans grow, soil is regularly tilled or disturbed during harvest time, green bean roots rarely make it past 8 inches in depth.
As they run alongside one another beneath the surface of the soil, each root will spread out laterally up to 10 feet apart from its neighboring root fibers.
Factors That Affect the Depth of Green Bean Roots
Growers can get the most out of their crops by knowing how different factors affect root growth. There are several factors that can affect the depth of green bean roots.
- The most important factor is the type of soil in which the plant is growing. Different types of soil have different levels of moisture, nutrients, and compaction, all of which can impact the depth of the roots. For example, sandy soil tends to drain well and is easy for roots to grow through, while clay soil can be harder for roots to grow through because it is more compact.
- Another factor that can affect the depth of green bean roots is the age of the plant. As a green bean plant grows and matures, its roots will also grow and develop. This means that the roots of a mature plant may be deeper than the roots of a younger plant.
- The amount of water and nutrients available in the soil can also affect root growth. If a plant is well-watered and has access to plenty of nutrients, its roots may grow deeper in search of these resources.
- Finally, the type of green bean plant can also impact the depth of its roots. Different varieties of green beans may have different root structures and growth habits, which can affect how deep their roots grow. For example, some varieties may have deeper roots than others, while others may have more shallow roots that are better suited to growing in drier or more compact soils.
Overal, the depth of green bean roots can be affected by a range of factors, including the type of soil, the age of the plant, the availability of water and nutrients, and the variety of green bean being grown.
Can Green Bean Grow in Shallow Soil?
Shallow soil may cause difficulty for plants when it comes to getting access to nutrients and water. The roots of green beans require enough space to spread out and take advantage of these resources.
In general, green beans need well-draining soil with a good balance of moisture and air in order to thrive. This means that they may not be well-suited to growing in shallow soil, which can be prone to drying out quickly or becoming waterlogged.
However, it is possible for green beans to grow in shallow soil if certain conditions are met. For example, if the soil is amended with compost or other organic matter to improve its structure and drainage, green beans may be able to grow in shallow soil.
Additionally, if the plants are watered regularly and provided with sufficient nutrients, they may be able to overcome the challenges of shallow soil and grow successfully.
Overall, while green beans can potentially grow in shallow soil, they are likely to have better success if grown in soil that is at least 12 to 18 inches deep. This will provide the plants with the moisture, nutrients, and support that they need to grow and produce a healthy harvest.
Tips for Encouraging Deep Root Growth in Green Bean Plants
Encouraging deep root growth in green bean plants can help to ensure that the plants have access to a sufficient supply of water and nutrients, leading to healthy growth and a successful harvest. Here are a few tips for encouraging deep root growth in green bean plants:
- Plant in well-draining soil: Green bean roots need access to moisture in order to grow, but they can be easily damaged by waterlogged soil. To encourage deep root growth, it is important to plant green beans in well-draining soil that has a good balance of moisture and air.
- Provide adequate watering: Green beans need regular watering to thrive, but it is important not to overwater them. Overwatering can lead to the development of fungal diseases, which can damage the roots and hinder their growth. To encourage deep root growth, water green bean plants deeply, but allow the soil to dry out slightly between waterings.
- Apply compost or other organic matter: Adding compost or other organic matter to the soil can help to improve its structure and drainage, making it easier for roots to penetrate deeply. This can also provide the plants with a source of nutrients, which can help to support healthy root growth.
- Avoid compacting the soil: Green bean roots need access to air in order to grow, and compacted soil can make it difficult for roots to penetrate deeply. To avoid compaction, avoid walking or working on the soil when it is wet, and use raised beds or other techniques to help prevent compaction.
By following these tips above, you can help to encourage deep root growth in your green bean plants, leading to healthier, more productive plants.