What Is the Difference Between Topsoil and Subsoil?
In the world beneath our feet lies a complex and fascinating ecosystem of soil, with each layer playing a unique role in supporting life on Earth. Two critical layers in this soil profile are topsoil and subsoil. While they may seem similar at a glance, delving deeper reveals stark differences that have a profound impact on everything from agriculture to construction.
In this article, we’ll dig into the world of topsoil and subsoil, exploring their compositions, depths, and roles in our environment. From the fertile topsoil teeming with life to the dense subsoil providing stability, we’ll unveil the secrets that make them unique.
By the end, you’ll possess the knowledge to make informed decisions, whether you’re cultivating a flourishing garden or laying the foundation for a new structure. Let’s dig in!
Introduction to Topsoil and Subsoil
Before we start distinguishing between topsoil and subsoil, let’s clarify what each term means:
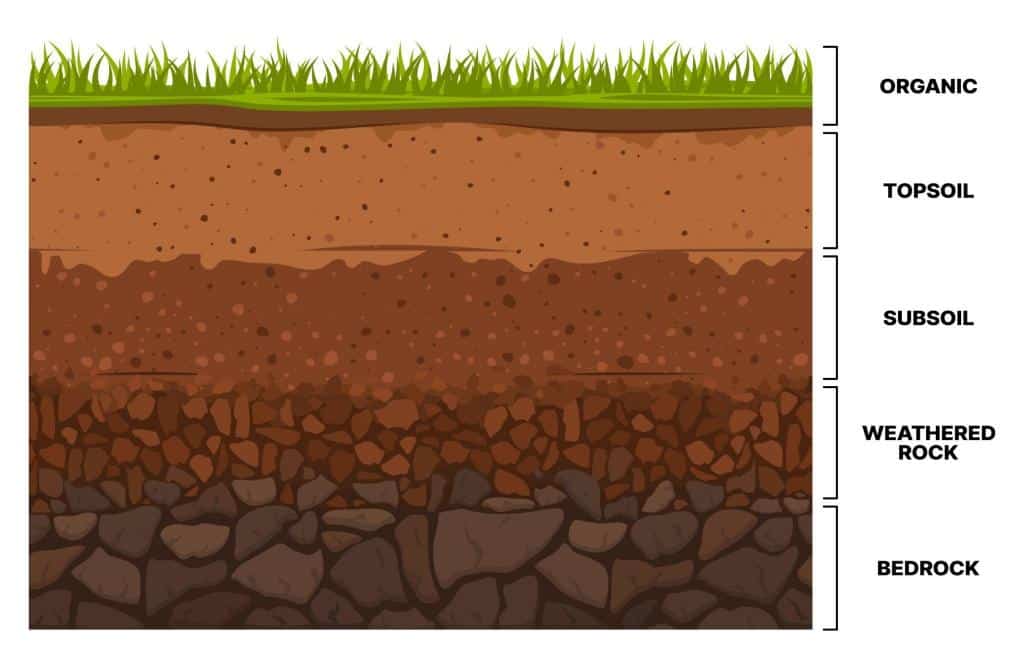
- Topsoil: Topsoil is the uppermost layer of soil, usually the first 5 to 12 inches deep, though it can vary depending on location and land use. It’s rich in organic matter, teeming with life, and the primary medium for plant growth.
- Subsoil: Subsoil lies just beneath topsoil, extending several feet below the surface. It contains fewer organic materials and is primarily composed of minerals.
Understanding the difference between topsoil and subsoil is crucial for various reasons:
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on topsoil for crop cultivation, as it is the most fertile layer. Knowing how to preserve and enhance topsoil quality is essential for food production.
- Construction: Builders need to consider the characteristics of subsoil when planning foundations and structures. Inadequate knowledge can lead to structural issues.
- Environmental Conservation: Soil erosion and land management practices depend on recognizing the distinctions between these soil layers.
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork, let’s explore the composition of topsoil in detail.
Topsoil: The Uppermost Layer of Earth
Topsoil, as the name suggests, is the uppermost layer of soil, typically ranging from 2 to 12 inches in depth. It’s the part of the soil that’s teeming with life – full of organic matter, nutrients, and microorganisms. Think of it as the Earth’s pantry for plants. Here are the key characteristics of topsoil:
1. Rich in Organic Matter

One of the defining features of topsoil is its richness in organic matter. This organic matter includes decomposed leaves, plants, and various microorganisms. Top soil contains humus and other organic matter. This abundance of organic material makes topsoil fertile, providing plants with the nutrients they need to thrive.
2. Ideal for Plant Growth
Because of its nutrient content, topsoil is the layer where most plants establish their roots. It offers the right balance of minerals and organic matter, creating a nurturing environment for seeds to germinate and plants to grow strong.
3. Dark in Color
Topsoil is typically darker in color compared to subsoil. This dark hue is a result of the organic matter it contains. The organic matter also gives topsoil a loose, crumbly texture, which is ideal for root penetration.
More: How to Identify Black Cotton Soil Effectively
4. Vulnerable to Erosion
Topsoil is more vulnerable to erosion from wind and water due to its loose texture. This can be problematic for agriculture and gardening, as it can lead to the loss of valuable nutrients.
5. Used for Gardening and Landscaping
Given its fertility and suitability for plant growth, topsoil is often used in gardening and landscaping projects. When you see lush green lawns and thriving flower beds, it’s usually because topsoil has been added to enhance the soil’s quality.
Subsoil: Beneath the Surface
Subsoil, on the other hand, lies beneath the topsoil and extends much deeper into the Earth. It can range from a few inches to several feet in depth, depending on the location. Subsoil serves a different set of purposes compared to topsoil:
1. Low in Organic Matter
Unlike topsoil, subsoil contains significantly less organic matter. It’s mainly composed of weathered rock fragments and minerals. This makes the subsoil less fertile and less conducive to plant growth.
2. Harder and More Compact
Subsoil is often denser and more compact than topsoil, making it challenging for plant roots to penetrate deeply. This is why plants primarily rely on topsoil for nutrients and anchoring.
3. Important for Drainage
While subsoil may not be ideal for growing plants, it plays a crucial role in drainage. Its compact nature allows it to channel excess water away from the root zone, preventing waterlogged conditions.
4. Stability for Structures
Subsoil’s density and stability make it valuable in construction. It provides a solid foundation for buildings, roads, and other structures. Engineers and builders often assess the subsoil’s composition before starting construction projects.
5. Less Affected by Erosion
Because of its compactness, subsoil is less vulnerable to erosion than topsoil. It provides a protective layer beneath the fertile topsoil, helping to preserve the nutrients and structure of the upper layers.
Key Differences Between Topsoil and Subsoil
To summarize, let’s take a look at the key differences between topsoil and subsoil in a convenient table:
| Aspect | Topsoil | Subsoil |
| Depth | 2 to 12 inches | Below topsoil, deeper into the ground |
| Organic Matter | Abundant | Low |
| Color | Dark | Often lighter in color |
| Texture | Loose and crumbly | Dense and compact |
| Plant Growth | Ideal for plant growth | Less conducive to plant growth |
| Erosion Vulnerability | Susceptible to erosion | Less affected by erosion |
| Drainage | Less effective in drainage | Important for drainage |
| Structural Use | Not suitable for construction | Provides stability for structures |
When to Use Each: Practical Applications
Understanding when to use topsoil and subsoil is crucial for successful gardening, landscaping, and construction projects.
When to Use Topsoil
- Gardening: Topsoil is a must for creating fertile gardens, flower beds, and vegetable patches.
- Landscaping: Use it to establish healthy lawns, plant shrubs, and trees.
- Soil Enhancement: When your existing soil lacks nutrients, adding topsoil can improve its quality.
When to Use Subsoil
- Construction: Subsoil is vital for providing a stable foundation for buildings and infrastructure.
- Drainage: In areas prone to waterlogging, subsoil helps direct excess water away from the surface.
- Road Construction: It’s used as a base layer in road construction to create a solid, durable surface.
Conclusion
In summary, topsoil and subsoil are two distinct layers of the earth with different properties and functions. Topsoil is the fertile upper layer, ideal for plant growth, while subsoil lies beneath, offering stability and drainage benefits.
Knowing the difference between the two is essential for making informed decisions about gardening, landscaping, and construction projects. Whether you’re nurturing a garden, building a home, or planning a landscaping project, understanding the roles of topsoil and subsoil is the key to success.
FAQs on Gardening with Topsoil and Subsoil
What is the difference in color between topsoil and subsoil?
Topsoil is typically darker in color due to its high organic matter content, while subsoil is often lighter in color because it contains fewer organic materials.
How can I test the quality of the topsoil and subsoil in my garden?
To test soil quality, use a soil testing kit or send samples to a local agricultural extension office. They can analyze nutrient levels, pH, and other factors for both topsoil and subsoil in your garden.
Is subsoil less fertile than topsoil for gardening?
Yes, subsoil is generally less fertile than topsoil for gardening due to its lower organic matter content and nutrient concentration. Plant roots primarily rely on topsoil for nutrients.
Can topsoil be replenished or improved over time?
Topsoil can be replenished and improved by adding organic matter like compost or mulch. Over time, these amendments enhance fertility, making it more conducive to plant growth.
Are there any plants that thrive specifically in subsoil?
Some deep-rooted plants, like trees and shrubs, can access nutrients from the subsoil. However, most garden plants rely on topsoil for their nutrient needs.
What are the common methods for preventing topsoil erosion?
Common methods for preventing topsoil erosion include planting cover crops, using mulch, creating terraces, and installing erosion control structures like silt fences.
Can subsoil be used as a substitute for topsoil in gardening?
Subsoil in Gardening: Subsoil is generally not suitable as a substitute for topsoil in gardening due to its lower fertility and poor drainage characteristics.





