The Role of the Pedicel in Tomato Growth and Development

As any tomato grower will tell you, tomatoes have a life of their own. They stretch, bloom, and bear fruit with a rhythm and resilience that’s almost inspiring. One part of the plant that often gets overlooked is the humble pedicel.
If you’ve ever noticed the small “stem” that connects each tomato fruit to the main plant, then you’ve spotted the pedicel in action! But this little structure does so much more than hold the fruit—it plays a vital role in the life of a tomato plant.
So let’s go delve deeper into the pedicel’s significance and discover its hidden significance.et up close and personal with the pedicel and uncover why it’s more important than you might think.
What Exactly Is the Pedicel?
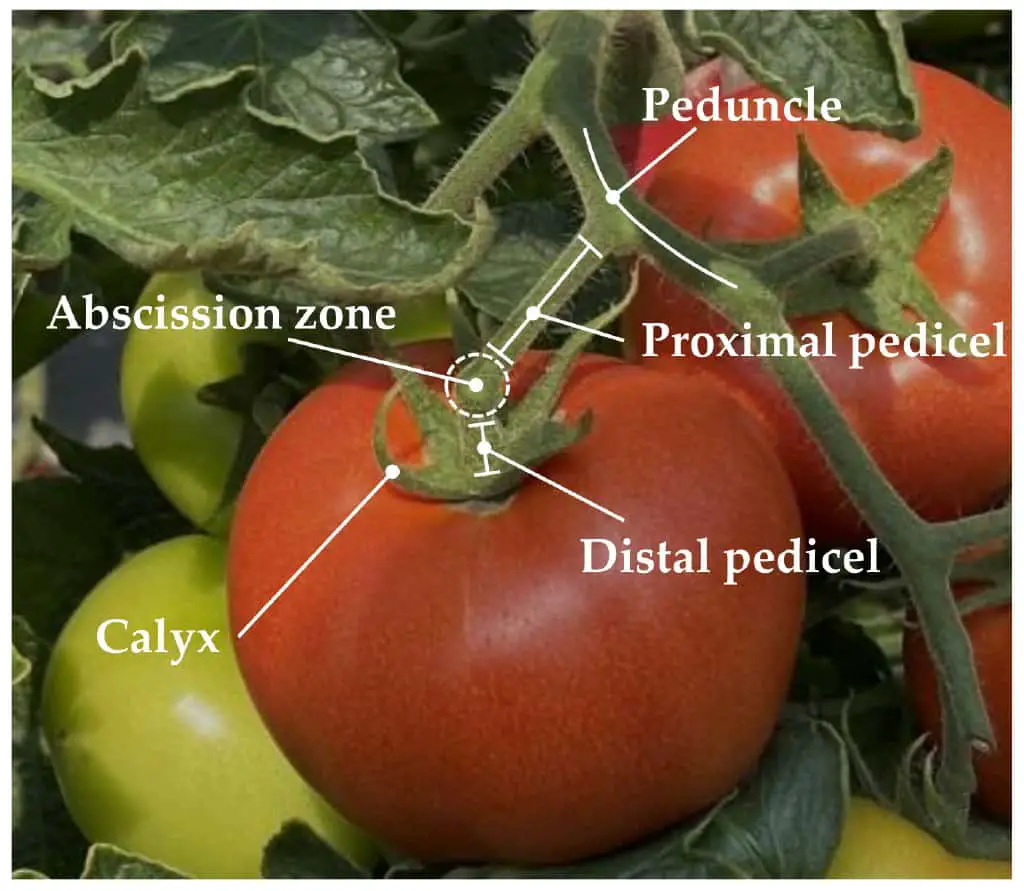
If you’re not familiar with plant anatomy, here’s the pedicel in a nutshell: it’s the slender stalk that connects a tomato flower, and later the fruit, to the main plant stem. Think of it as the “umbilical cord” of the tomato. The pedicel may seem like a minor part, but without it, the journey from flower to juicy, ripe tomato simply wouldn’t happen.
Quick Breakdown of Tomato Plant Structure
To appreciate the pedicel, let’s put it in the context of the tomato plant as a whole:
| Plant Part | Function |
| Main Stem | Supports the plant and transports nutrients |
| Leaves | Photosynthesis powerhouse, providing energy |
| Roots | Absorb water and nutrients from the soil |
| Pedicel | Connects the flower/fruit to the main stem, nutrient channel |
| Fruit | The ultimate goal: juicy, flavorful tomatoes! |
As a simple bridge, the pedicel doesn’t look like much. But it plays multiple roles that contribute to the tomato’s growth, health, and ripeness.
The Pedicel: More Than Just a Connector
So, what does the pedicel actually do? As it turns out, it’s much more than just a “holder” or “connector.” It’s a multitasking powerhouse.
1. Nutrient and Water Transport
Think of the pedicel as a superhighway for nutrients and water. After the plant absorbs water and nutrients from the soil, these resources travel up the main stem and into the pedicel, eventually reaching the developing tomato. Without the pedicel, this crucial transfer of resources wouldn’t occur, leaving the tomato starved and shriveled.
2. Hormonal Regulation
Plants have hormones too! And the pedicel plays a major role in delivering growth hormones to the developing fruit. One of these hormones, auxin, is critical for fruit growth and development. The pedicel regulates the levels of these hormones, ensuring that the tomato ripens properly and becomes plump and flavorful.
3. Protective Barrier
The pedicel serves as a protective barrier, helping to keep pathogens at bay. By acting as a “buffer” between the main plant and the fruit, it limits the spread of diseases and pests. So next time you see a healthy tomato, remember to thank the pedicel for holding the line against unwanted intruders.
| Read: Staking Tomato Plants: Tips and Tricks |
The Role of the Pedicel in Tomato Pollination
Pollination marks the beginning of fruit formation, and the pedicel plays a part in this as well. Once a tomato flower is pollinated, the pedicel goes into high gear, shifting its energy toward supporting the growth of the newly fertilized ovary. It begins to swell slightly, allowing more nutrients to flow through and start transforming the flower into a small green tomato.
How Pollination Affects the Pedicel
Successful pollination triggers changes in the pedicel’s structure and function. Here’s how it happens:
- Increased Nutrient Flow – After pollination, the pedicel ramps up its nutrient transport, providing the young fruit with everything it needs.
- Strengthening the Structure – The pedicel subtly strengthens to support the weight of the developing tomato, especially in varieties that bear larger fruit.
- Hormone Production – Pollination stimulates hormone production, which the pedicel helps to carry to the growing fruit.
Essentially, pollination provides the pedicel with instructions, and it responds by ensuring the fruit has the necessary resources to grow.
Can Problems in the Pedicel Affect Tomato Growth?
Absolutely! If the pedicel is damaged or diseased, it can stunt or even halt the growth of the tomato fruit. Here are a few issues that can arise and impact your tomato harvest.
1. Pedicel Breakage
Sometimes, strong winds or improper handling can break the pedicel. This cuts off the supply of nutrients and water to the fruit, leading it to shrivel and drop. When pruning or harvesting, it’s essential to handle the plant gently to avoid damaging these fragile connections.
2. Disease Transmission
Diseases like blossom end rot or fruit blight can spread through the pedicel if the plant isn’t healthy. Since the pedicel connects directly to the fruit, any disease present in the main plant can potentially transfer through the pedicel.
3. Hormone Imbalance
If the pedicel doesn’t regulate hormones effectively, it can lead to issues like uneven ripening or deformed fruit. The right balance of growth hormones is essential for the tomato’s color, flavor, and texture.
Pruning and Caring for the Pedicel: Best Practices
Although we don’t typically think about pruning the pedicel, there are ways to care for this part of the plant to encourage healthy fruit development. Here are some best practices:
1. Prune with Care
While the pedicel itself doesn’t require pruning, any nearby leaves or stems should be pruned carefully to avoid accidental damage. Use sharp, clean tools to prevent breakage and disease transmission.
2. Provide Adequate Support
Tomato plants often need a sturdy cage or trellis to keep the fruits off the ground. Proper support reduces strain on the pedicel, especially when the tomatoes start to ripen and weigh down the branches.
3. Monitor for Pests and Disease
Inspect the plant regularly for any signs of disease or pests. Early detection can prevent diseases from spreading through the pedicel to the fruit, saving your harvest.
4. Water Consistently
Watering regularly keeps the plant’s vascular system, including the pedicel, functioning well. Irregular watering can lead to nutrient imbalances and stress on the plant, affecting the pedicel’s role in fruit growth.
How Different Varieties Depend on the Pedicel
Some tomato varieties rely on the pedicel more than others, particularly heavy fruiting types. Let’s take a look at a few examples:
| Tomato Variety | Pedicel Requirements |
| Cherry Tomatoes | Light pedicel support, smaller fruit size |
| Beefsteak Tomatoes | Requires strong pedicels for heavy fruit clusters |
| Roma Tomatoes | Moderate pedicel strength, bushy growth habit |
| Heirloom Varieties | Varies, but often requires robust pedicels |
Larger varieties, like beefsteak tomatoes, depend on a strong pedicel to support their weight. Cherry tomatoes, on the other hand, put less strain on their pedicels, thanks to their small, lightweight fruits.
| Check out: Can You Grow Tomatoes Year Round in Florida? |
Final Thoughts: The Unsung Hero of Tomato Growth
The pedicel may be small, but it’s anything but insignificant. Without this little “stem,” our tomatoes wouldn’t be able to thrive, much less develop that juicy, red, mouth-watering quality we love. It quietly does the heavy lifting—transporting nutrients, fighting off disease, and even influencing the final flavor of the fruit.
So next time you’re out in the garden, take a moment to appreciate the pedicel. This unassuming stalk is one of the keys to tomato success, and by understanding its role, we can become better caretakers for our plants. Whether you’re growing cherry tomatoes or hefty beefsteaks, a healthy pedicel can make all the difference between a bountiful harvest and a disappointing season.
In the world of gardening, it’s often the smallest players that have the biggest impact. And when it comes to tomatoes, the pedicel truly is the unsung hero.






