Why Should You Not Buy Caged Eggs? (Health & Ethical Concerns)

Eggs are a staple in many households, prized for their versatility and nutritional value. However, not all eggs are created equal. A significant distinction exists between caged eggs and those from more humane sources.
Are you aware of what goes into the eggs you buy? The debate between caged and cage-free eggs extends beyond just the price tag. Have you ever wondered why caged eggs are becoming less popular among consumers?
This article dives into the health risks of caged eggs. It also covers the ethics of their production and the benefits of cage-free options.
The Reality of Caged Egg Production

Caged eggs come from hens confined in small wire cages, often with minimal space to move. This is industrial farming. It’s called battery cage farming. It prioritizes quantity over quality. It harms the hens and the consumers who eat their eggs.
Conditions of Caged Hens
Hens in battery cages endure extremely cramped conditions, often with less space than an A4 sheet of paper per bird. These environments lead to high stress, feather loss, and increased susceptibility to disease.
The hens lack natural behaviors. These include nesting, perching, and dust-bathing. This lack causes the hens much physical and psychological distress.
Impact on Egg Quality
The stressful environment of battery cages affects the quality of the eggs produced. Research shows that caged hens often lay eggs with thinner shells. The eggs also have higher levels of contaminants and less nutrition than those from free-range or organic systems. These eggs might be more prone to breakage and contamination, posing potential health risks to consumers.
Health Consequences of Consuming Caged Eggs
Consuming caged eggs can pose various health risks due to the conditions in which the hens are kept. These concerns are significant enough to warrant a shift towards more ethically produced eggs.
Higher Risk of Contamination
Caged hens have a higher risk of Salmonella infection due to the stressful and unsanitary conditions of battery cages. Salmonella can contaminate the eggs and cause foodborne illnesses in humans.
Studies have shown that eggs from caged systems are more likely to have this dangerous bacterium. This is compared to eggs from hens kept in natural, spacious environments.
Nutritional Differences
Eggs from free-range or organic hens tend to have better nutritional profiles. They often contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A and E, and lower levels of cholesterol.
Caged hens have a limited diet and lifestyle. They eat processed feed and can’t forage. This leads to eggs that are less nutritious than those from hens with access to pasture and a varied diet.
Ethical Concerns of Caged Eggs
Beyond health, the ethical implications of caged egg production are profound. The welfare of hens in these systems is severely compromised, raising significant moral questions.
Animal Welfare Issues
The inhumane treatment of hens in battery cages is a primary ethical concern. These hens suffer from extreme confinement, unable to engage in natural behaviors. The stress and physical toll of such conditions often lead to early mortality and poor health, highlighting the moral cost of cheap eggs.
Environmental Impact
Caged egg production also has a notable environmental footprint. Battery cage farming is intensive. It needs lots of resources: feed, water, and energy. It also makes lots of waste and pollution. In contrast, sustainable egg farming uses free-range or organic systems. These have lower environmental impacts and promote better land stewardship.
The Alternatives: Free-Range and Organic Eggs
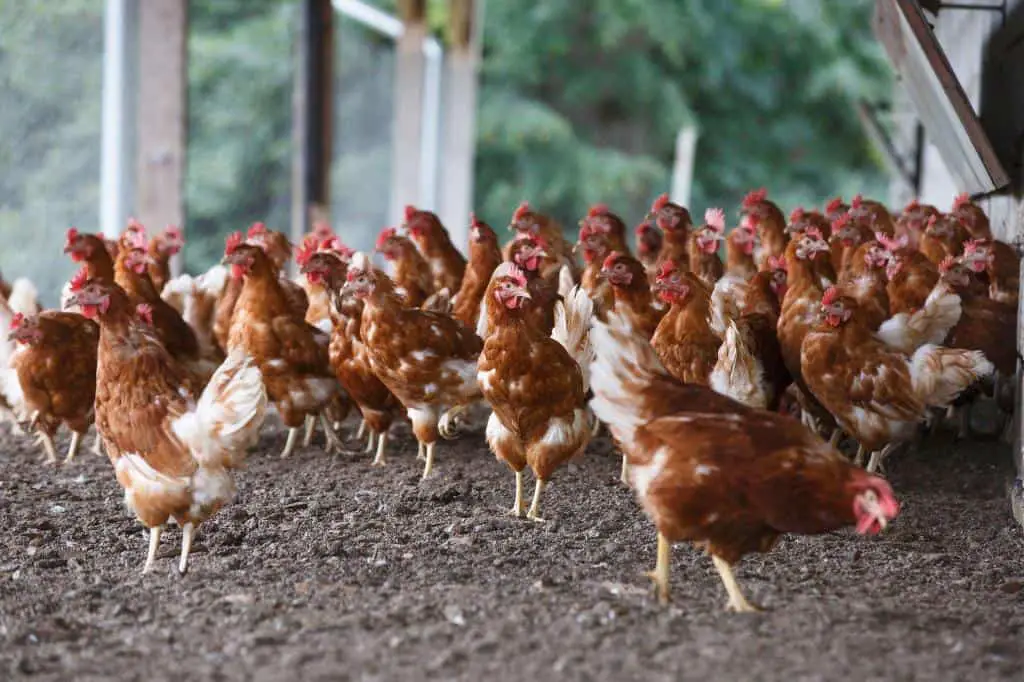

Choosing eggs from free-range or organic sources can reduce many of the health and ethical concerns. These concerns are associated with caged eggs. These alternatives offer a more humane and sustainable approach to egg production.
Free-Range Eggs
Free-range eggs come from hens. They have access to the outdoors, so they can do natural things like foraging, dust-bathing, and nesting. These hens have better living conditions and health. This results in eggs that are both ethical and high quality.
Organic Eggs
Organic eggs take the benefits of free-range systems a step further. In addition to outdoor access, organic hens are fed an organic diet free from synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and GMOs. These eggs are produced under strict welfare standards. They ensure the highest level of animal care and environmental sustainability.
| Read: When Do Pekin Ducks Start Laying Eggs and How Often? |
Making the Switch: Practical Tips for Consumers
Transitioning to free-range or organic eggs can seem daunting, especially given the higher price tags. However, the benefits far outweigh the costs. Here are some practical tips for making the switch.
Understanding Labels
Navigating egg labels can be confusing. Look for certifications such as “Certified Humane,” “Animal Welfare Approved,” and “USDA Organic.” They ensure you are buying ethically produced eggs. These labels guarantee the eggs come from hens. The hens were raised in humane and eco-friendly conditions.
Budget-Friendly Strategies
While free-range and organic eggs are more expensive, there are ways to manage the cost. Consider buying in bulk. Also, seek out local farmers’ markets or join a community-supported agriculture (CSA) program. These options often offer fresher, higher-quality eggs at more affordable prices.
Reducing Consumption
Another way to afford better eggs is to reduce overall consumption. Treat eggs as a premium ingredient, not a daily staple. This way, you can enjoy high-quality eggs without raising your grocery bill.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions about the egg industry that can make the transition to humane eggs challenging. Let’s address some of these myths.
“All Eggs Are the Same”
Not all eggs are created equal. The conditions in which hens are raised directly impact the quality and safety of the eggs they produce. Free-range and organic eggs are clearly better. They are better in both nutrition and ethics.
“Caged Eggs Are More Affordable”
While caged eggs are cheaper at the checkout, they come with hidden costs. Caged eggs have health risks and ethical concerns. They can cause higher long-term expenses, including medical bills and environmental cleanup costs.
“It’s Hard to Find Humane Eggs”
Humane eggs are increasingly available as consumer demand for ethically produced food grows. Many supermarkets now sell free-range and organic eggs. Farmers’ markets offer direct access to humane and sustainable egg producers.
The Future of Egg Production
The trend towards more humane and sustainable egg production is gaining momentum. Consumers are more aware of the issues with caged eggs. The demand for free-range and organic options is rising.
Industry Shifts
Many companies and retailers are pledging to adopt cage-free policies. This signals a big change in the egg industry. The changes reflect consumer concern for animal welfare. They also show a desire for sustainable food systems.
Supporting Change
By choosing humane eggs, consumers can drive positive change in the industry. Supporting brands and farmers that prioritize animal welfare and sustainability encourages more producers to adopt humane practices. This will lead to a better future for both hens and humans.
Conclusion
The decision to avoid caged eggs is rooted in both health and ethical considerations. Choose free-range or organic eggs. They are better quality and support humane, sustainable farming. The benefits of switching are clear. It offers better food, improved animal welfare, and a smaller environmental footprint.
As consumers, our choices have the power to shape the future of the food industry. We can promote a better world by prioritizing ethically produced eggs. They are more compassionate and sustainable.