Do Brussel Sprouts Need Stakes or Cages Support to Grow?

Are you ready to embark on a culinary adventure in your garden? Brussel sprouts, those adorable miniature cabbages, have captured the hearts and taste buds of many in recent years. But as you prepare to cultivate these delightful vegetables, a question arises: do Brussel sprouts need stakes or cages for support as they grow?
In this green-thumb guide, we’ll unravel the mystery and provide you with the knowledge you need to nurture thriving Brussel sprout plants. We’ll explore the nature of these cool-season crops, their vertical growth habits, and the potential benefits of offering them a helping hand. From stability and protection to improved air circulation and easier harvesting, we’ll delve into the advantages of supporting your Brussel sprouts.
So grab your gardening gloves and get ready to discover whether staking or caging is the secret ingredient to success for your Brussel sprouts. Prepare to transform your garden into a vibrant haven of these delectable delights as we uncover the secrets of their growth and offer insights into the best methods for support. Let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of Brussel sprout cultivation!
Introduction to Brussel Sprouts
Before we delve into the question of support for Brussel sprouts, let’s first understand the nature of these plants. Brussel sprouts, scientifically known as Brassica oleracea var. gemmifera, belong to the Brassicaceae family. They are cool-season crops that thrive in temperate climates.
Brussel sprouts are known for their vertical growth habit, with a single tall stem that gives rise to compact leafy heads or “sprouts.” These sprouts develop in the leaf axils along the stem and grow larger as the plant matures. Given their vertical nature, Brussel sprouts may require support as they grow to prevent them from toppling over or breaking under their own weight.
Understanding the Growth Habits of Brussel Sprouts
To comprehend the need for support in Brussel sprouts, it is crucial to understand their growth habits. Brussel sprouts go through distinct stages of growth and development, each with its own unique characteristics and requirements.
During the initial stage, Brussel sprouts form a sturdy central stem with leaves arranged in a spiral pattern. As the plants mature, side shoots develop in the leaf axils, which eventually grow into the sprouts we harvest. These side shoots continue to elongate, producing more sprouts over time.
The growth habit of Brussel sprouts plays a significant role in determining their need for support. As the plants grow taller, they become increasingly top-heavy, making them susceptible to bending, breaking, or even uprooting. Providing support becomes essential to maintaining the integrity of the plants and ensure their productivity.
The Need for Support For Optimal Growth
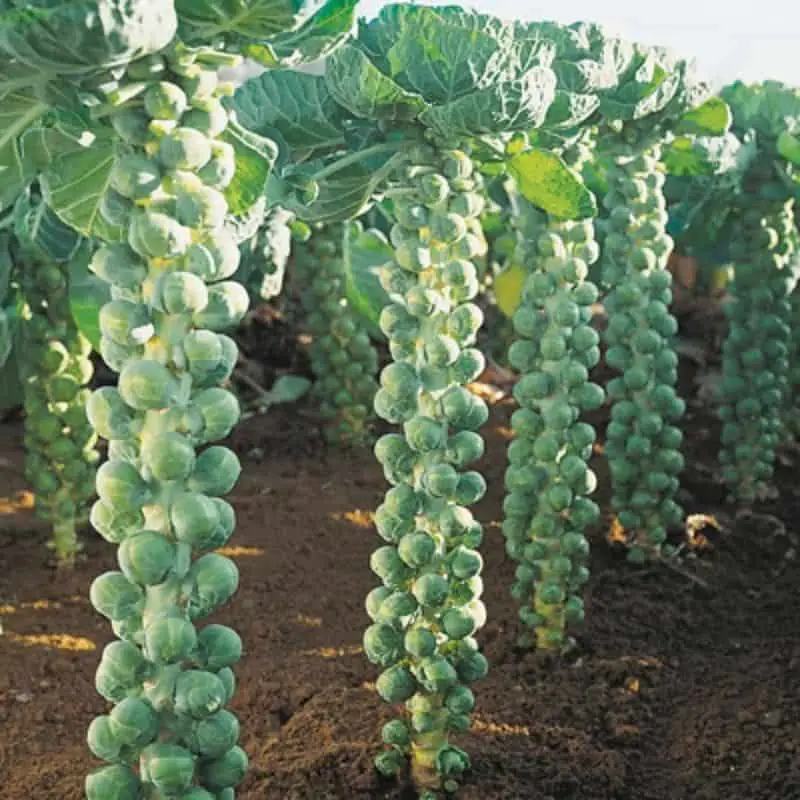

In general, Brussel sprouts do not absolutely require stakes or cages for support. However, providing support can offer several advantages that contribute to healthier plants and higher yields.
1. Stability and Protection
Brussel sprout plants can grow quite tall, reaching heights of up to three feet or more. As the sprouts mature and develop, they exert additional weight on the main stem, which may make the plant top-heavy and prone to bending or snapping. Using stakes or cages can provide stability and prevent these mishaps, protecting your precious sprouts from damage.
2. Air Circulation
Another benefit of using support for Brussel sprouts is improved air circulation. When the plants are grown densely without support, their leaves may become crowded, impeding airflow and creating a conducive environment for pests and diseases. Stakes or cages allow for better airflow between the plants, reducing the risk of fungal infections and other issues.
3. Accessibility and Ease of Harvesting
Supporting your Brussel sprout plants makes it easier to access the sprouts when they are ready for harvest. By elevating the plants slightly off the ground, you can prevent the sprouts from touching the soil, reducing the risk of soil-borne diseases. Additionally, the elevated sprouts are more visible and easily reachable, simplifying the harvesting process.
Factors Influencing the Need for Support in Brussel Sprouts
Various factors contribute to the need for support in Brussel sprouts. Understanding these factors will help you assess whether stakes or cages are necessary for your plants.
1. Plant height and size
Different varieties of Brussel sprouts exhibit varying heights and sizes. Some cultivars can reach impressive heights, often exceeding three feet. Taller plants are more prone to toppling over due to their increased weight and vulnerability to strong winds. It is advisable to provide support for these larger plants to ensure their stability and prevent damage.
2. Weather conditions and wind exposure
Brussel sprouts thrive in cool climates, but they can also tolerate moderate heat. However, strong winds can wreak havoc on these delicate plants. Wind exposure can lead to bending and breakage of the stems, adversely affecting the plant’s health and productivity. If you live in an area prone to high winds, it is wise to provide support to safeguard your Brussel sprouts.
3. Soil fertility and health
The quality of the soil in which your Brussel sprouts grow also influences their need for support. Brussel sprouts require well-drained, fertile soil that is rich in organic matter. Soil that lacks nutrients or has poor structure can result in weak root systems and less sturdy plants. In such cases, providing support can help compensate for the weaker growth and prevent the plants from toppling over.
Choosing the Right Support Method
When it comes to supporting Brussel sprouts, you have several options to choose from. The most common methods involve using stakes or cages. Let’s take a closer look at each method and its benefits.
1. Stakes
Stakes are vertical supports that are typically made of wood, bamboo, or metal. They are driven into the ground near the base of the plants and provide a sturdy framework for the Brussel sprouts to lean on. Staking Brussel sprouts involves tying the main stem of each plant to the stake using soft plant ties or twine.
Advantages of Stakes:
- Provides individual support to each plant, allowing for better customization.
- Easier access to the plants for maintenance tasks like pruning and harvesting.
- Cost-effective option, especially if you can source stakes from your own backyard or local resources.
Disadvantages of Stakes:
- Requires more effort during installation and tying of the plants.
- Limited in height, which may pose challenges for extremely tall varieties.
- May require additional support, such as crossbars or horizontal strings, as the plants grow taller.
Cages
Cages are three-dimensional structures made of wire or plastic, resembling a cylinder or cone shape. These cages are placed over the young Brussel sprout plants, providing all-around support as they grow. Caging Brussel sprouts involves simply inserting the cage over the plants, allowing them to naturally grow through the openings.
Advantages of Cages:
- Provides 360-degree support, protecting the plants from all sides.
- Can accommodate taller varieties without the need for additional support.
- Requires minimal effort during installation, as the plants naturally grow through the cage.
Disadvantages of Cages:
- Bulkier and take up more space in the garden compared to stakes.
- Relatively higher cost if purchasing cages, especially for larger gardens.
- Limited customization, as all plants within a cage receive the same support.
3. Hybrid Methods
In some cases, gardeners combine staking and caging methods for optimal support. This hybrid approach involves placing individual cages around each plant and securing them to stakes driven into the ground. This method provides the benefits of both staking and caging, offering maximum stability and protection for your Brussel sprouts.
Steps to Stake Brussel Sprouts
Staking Brussel sprouts involves providing vertical support to the plants using stakes and securing them in place. Follow these step-by-step instructions:
- Preparation of the planting area: Before planting your Brussel sprouts, prepare the soil by removing any weeds and loosening it to improve drainage. Ensure the planting area receives adequate sunlight.
- Installation of stakes and tying the plants: Place the stakes into the ground, positioning them near the base of each Brussel sprout plant. The stakes should be tall enough to accommodate the expected height of the plants. Gently tie the main stem of each plant to the stake using soft plant ties or twine. As the plants grow taller, continue tying them at regular intervals to provide additional support.
Steps to Cage Brussel Sprouts
Caging Brussel sprouts involves enclosing the plants within wire or plastic cages to provide all-around support. Here’s how to cage your Brussel sprouts:
- Choosing the appropriate cages: Select cages that are tall enough to accommodate the expected height of the Brussel sprout plants. Ensure the openings in the cages are wide enough for the plants to grow through. Wire or plastic cages with a cylindrical or cone shape work well for this purpose.
- Proper installation and securing of the cages: Place the cages over the young Brussel sprout plants, ensuring they are centered and stable. As the plants grow, guide them through the openings in the cages, allowing them to naturally grow within the structure. Secure the cages to the ground if necessary, using stakes or pegs, to prevent them from toppling over in strong winds.
Conclusion
While Brussel sprouts do not necessarily require stakes or cages for growth, providing support offers numerous benefits. Stakes or cages contribute to the stability and protection of the plants, improve air circulation, and facilitate easier harvesting. Depending on the variety and growth habit of your Brussel sprouts, you can choose between staking, caging, or a hybrid approach to provide the necessary support.
Remember to consider the specific needs of your Brussel sprout plants when selecting a support method. Implement the support early in the growth process and monitor the plants regularly to ensure they are adequately supported. With the right support, you can cultivate healthy and bountiful Brussel sprouts that will delight your taste buds and provide a visual treat in your garden. Happy gardening!
FAQs
What happens if you don’t support Brussel sprouts?
If you don’t support Brussel sprouts, they may become top-heavy and prone to bending or snapping, especially as the sprouts develop and add weight to the plant. Lack of support can lead to damage, reduced stability, and lower yields.
Can I use tomato cages for Brussel sprouts?
Yes, tomato cages can be used for Brussel sprouts. While they are designed for tomatoes, they can provide support for bushier or sprawling varieties of Brussel sprouts. Ensure that the cages are tall enough to accommodate the plants’ growth and securely place them around the plants.
When should I stake or cage my Brussel sprout plants?
Stake or cage your Brussel sprout plants early in their growth process, ideally when they are still young and establishing their root systems. This will ensure that the support is in place as the plants grow taller and the sprouts develop.
How tall do Brussel sprouts grow?
Brussel sprouts can grow to heights of up to three feet or more, depending on the variety. It’s important to consider the specific variety you are growing and provide support accordingly. Taller varieties may require taller stakes or cages for adequate support.
Are there any alternatives to staking or caging Brussel sprouts?
Yes, there are alternative methods to staking or caging Brussel sprouts. Some gardeners use trellises, bamboo poles, or even string netting to provide support. These methods can work well, especially for taller varieties or when space is limited.
Do Brussel sprouts need support in containers?
Brussel sprouts grown in containers can benefit from support. While the size of the container may restrict the use of traditional stakes or cages, you can still provide support by using smaller stakes or tying the plants to a trellis or other vertical structure within the container.
What are the potential problems if I don’t provide support for Brussel sprouts?
If you don’t provide support for Brussel sprouts, potential problems can arise. The plants may lean, bend, or break under the weight of the developing sprouts, leading to damage and reduced yield. Without proper support, the plants can also become overcrowded, impeding airflow and increasing the risk of pests and diseases. Additionally, the sprouts may touch the ground, making them more susceptible to soil-borne diseases.